
If length is longer than the first character_expression,ĭeletion occurs up to the last character in the last character_expression. Another way is using the CONCAT function. SQL Server does not support the operator for concatenation. Here’s an example using the + symbol: SELECT John + Smith AS fullname FROM dual Result: FULLNAME. Is an integer that specifies the number of characters to delete. String concatenation in SQL Server is done using the + symbol or the CONCAT function. If start is longer than the first character_expression, a null string is returned. If start or length is negative,Ī null string is returned. Is an integer value that specifies the location to start deletion and insertion. character_expression can be a constant, variable, or column of either A common usage of the CONCATWS () function is to create a comma-delimited list. If you just use the CONCAT () function, you’d have no separator (unless you explicitly added a separator as an argument between each string argument). The syntax for the CONCAT function is as shown below: CONCAT(Column 1, column 2. The query to create a table is as follows. select CONCAT (yourColumnName1, ,yourColumnName2) as anyVariableName from yourTableName To understand the above concept, let us create a table. STUFF functions looks like this : STUFF (character_expression, start, length ,character_expression ) In MySQL, the CONCATWS () function allows you to add a separator to concatenated strings. Concatenate Columns Using the CONCAT Function in MySQL The CONCAT function can concatenate or combine values from multiple columns into a single column. To concatenate two columns, use CONCAT () function in MySQL. In the first string at the start position and then inserts the second string into the first string
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/CONCATENATE_Syntax-5bd0d44fc9e77c0051e5ed72.jpg)
The new column Name is generated to store the concatenated string. It deletes a specified length of characters Execute the SELECT CONCAT command having column names in the brackets separated by a comma. The stuff function inserts a string into another string.
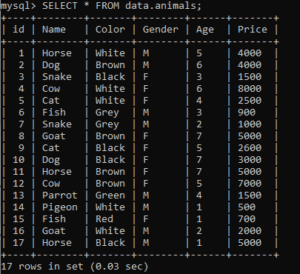
My table name is test, and for concatination I use the For XML Path('') syntax. Execute the upper disused syntax for the Person table. Then to create a cursor object, use the cursor () function.

#MYSQL ADD COLUMN WITH CONCATED DATA PASSWORD#
Pass the host, user (root or your username), password (if present), and database parameters to connect () method. Select distinct NAME, LIST = Replace(Replace(Stuff((select ',', +Value from test where name = _a.name for xml path('')), 1,1,''),'', ''),'','') from test _a order by 1 desc Steps are as follows: Use connect () function to establish a connection with the database server. IF OBJECT_ID('master.test') is not null Drop table test CREATE TABLE test (ID INTEGER, NAME VARCHAR (50), VALUE INTEGER )


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
